
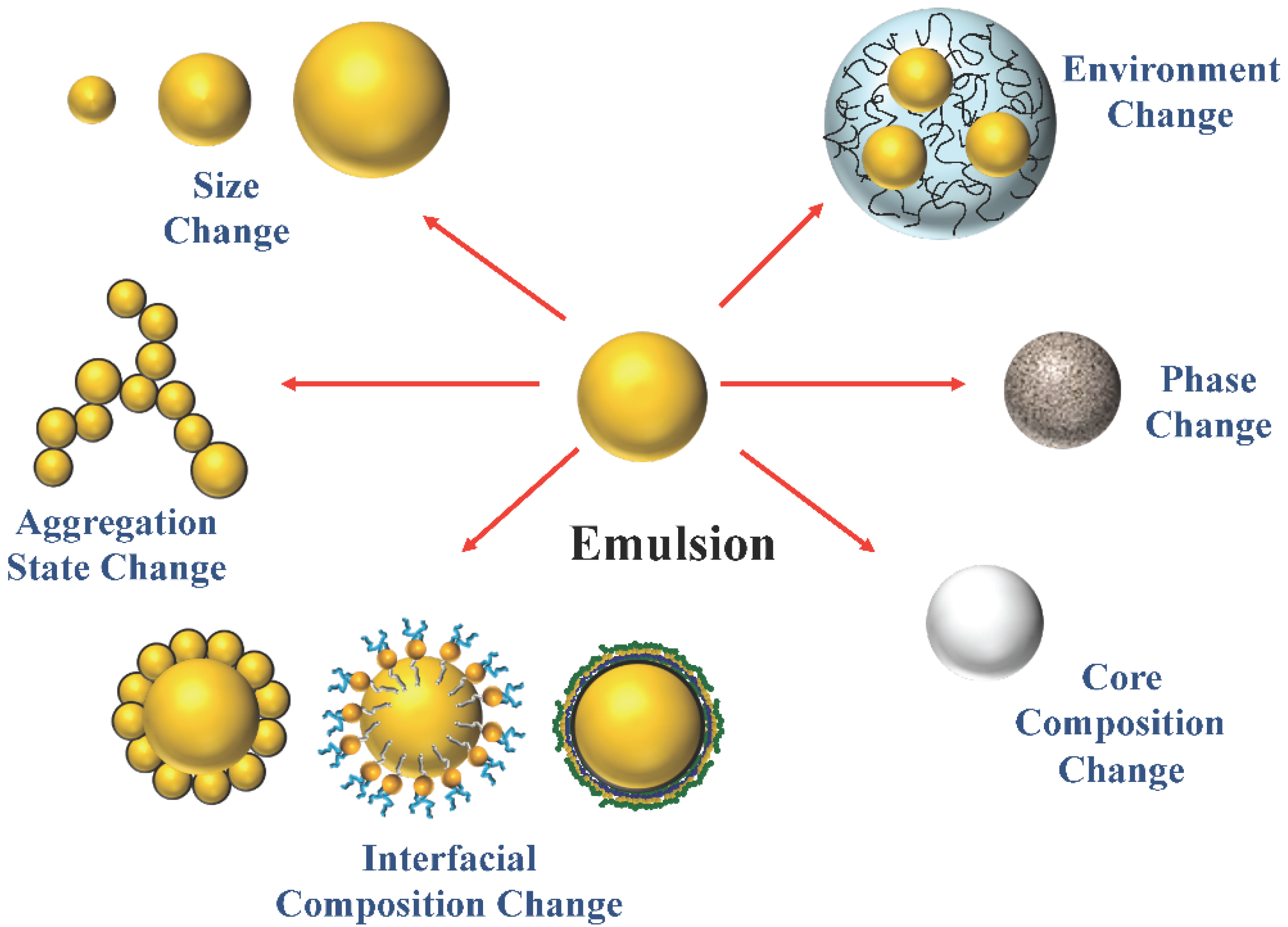
In addition to the examples mentioned above emulsions also exist in the form of salad. Emulsions are thicker than either the water or of fat/oil they contain, which is a useful property for some foods. Butter and margarine are common examples of water-in-oil emulsions.

By vigorously mixing the emulsifier with the water and fat/oil, a stable emulsion can be made.Ĭommonly used emulsifiers include egg yolk, or mustard. The hydrophilic end of the emulsifier molecule is attracted to the water and the hydrophobic end is attracted to the fat/oil. A classic cold cream cleanser is another example of a W/O emulsion. Yet within our home are numerous examples of. We are all familiar with the immiscibility of oil and water. The electric field can be applied by either direct current or alternating current. Milk is an example of an oil-in-water emulsion, while butter is water-in-oil. In a water-in-oil emulsion, the roles are switched. These help to form and stabilise the emulsions, preventing or slowing the water and fat/oil from separating.Įmulsifier molecules work by having a hydrophilic end (water-loving) and hydrophobic end (water-hating). Water-in-oil emulsions create more occlusive and water-resistant products such as sunscreen, foundation, diaper cream and weather shielding cream. However, some ingredients are generally immiscible. Electric-Field Separation In oilwater separation, electric field can very efficiently play its role where under the influence of an electric field, polarization of oil and water molecules quickly takes place. When an emulsion is oil-in-water, oil is the dispersed phase that is distributed into the continuous phase, water. Oil-in-water emulsions will mix readily with water-based liquids, while water-in-oil emulsions mix more easily with oils. To prevent the mixture from separating substances called emulsifiers can be added.

Emulsion Definition An emulsion is defined as a mixture of two or more normally immiscible (unmixable) liquids. Here is the emulsion definition, examples, types of emulsions, and a look at their uses. The HLB value of each surfactant is determined by an analysis of the characteristics of the surfactant. However the mixture is unstable and if you left it for a while it would soon separate out into water and oil layers again. An emulsion is one of the possible outcomes of mixing two liquids. Surfactants with a low HLB are more lipid loving and thus tend to make a water in oil emulsion while those with a high HLB are more hydrophilic and tend to make an oil in water emulsion. If you shake the oil and water together then the oil breaks up into tiny droplets and becomes distributed in the water forming a mixture. If you add a drop or two of oil to water you can see that it does not dissolve or combine with the water: the oil floats on the water.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
